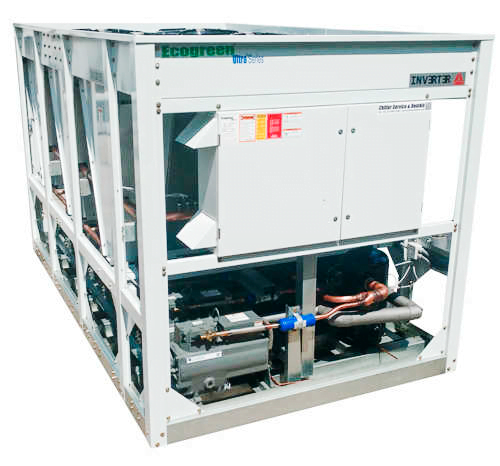
What is a Heat Recovery?
Heat Recovery systems are those that provide Cooling and Heating at the same time, which are developed for better sustainability in the energy field (energy savings).
In its operation, the heat is extracted and injected by the indoor units according to the components and the study prior to the manufacture of said system to achieve greater efficiency.
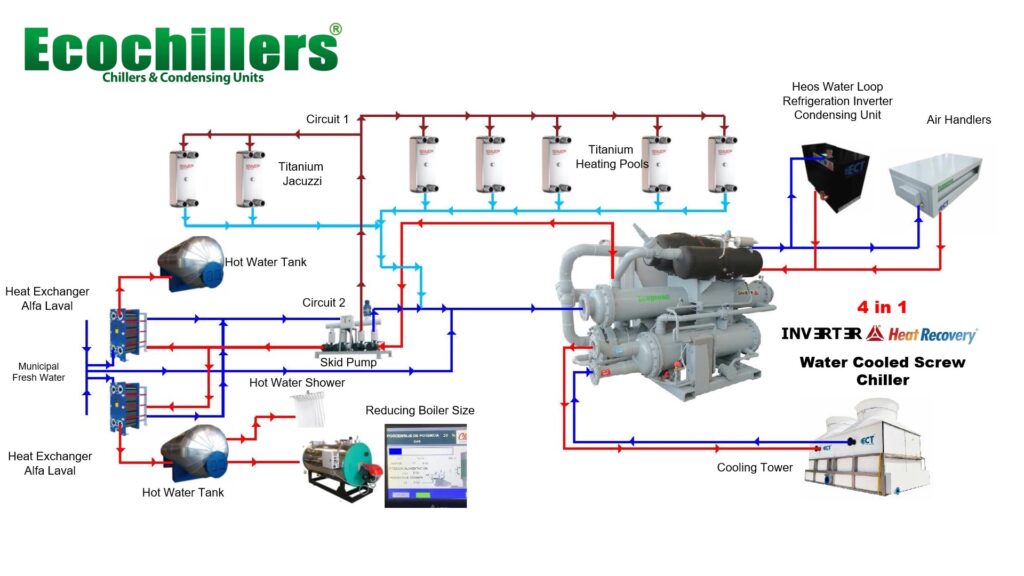
The chillers or Air handlers with Heat Recovery application work together with the external equipment as exchangers, in this way, working together, they can work both with cold and heat for Building Heating, Process Heating, Food Heating, Brewery, Distillery and at same time Cooling the process,
Most energy-efficient alternative to heaters
Heat Recovery offer the Most energy-efficient alternative to boilers, heaters, furnaces and air conditioners for all applications AC and process, like a chiller, heat recovery use electricity to make a cool space cool in summer or to cooling water and process dairy, products, vegetables, meat, poultry, but it can also generate or Recover the Heat Load equal to the Heat taked from the cooling process plus the heat generate by the compressor motor, during the cooling process transfer heat from the milk or any product or Air Conditioned spaces into Heating Load capable to reach 180°F temperature in water or even oil process.
Heat Recovery move heat from your air conditioning coils or process water loops turn in to Hot Water by FREE. Because they transfer Free heat rather than generate heat.
There are four main types of Heat Recovery Chillers or Package Units, connected by pipes: air-to-air, air-to-water, water-to-air, water-to-water. They collect heat from the cooling process and concentrate it for use in your heating water loop.
Ecogreen Heat Recovery
This technology heats and cools simultaneously between the hot water circuit, the cool water circuit and if its necessary to the air in case you don’t need all the Heat load or All the Cooling Load in some seasons. Ecogreen heat Recovery can reduce your electricity or Fuels use for heating by approximately 70% or more depending on the Process Cooling and Heating conditions compared to electric resistance or gas fired heat. It also eliminates the need for boilers that burn fuels and produce carbon emissions.
Ecogreen’s operating conditions offer a legitimate heating alternative in colder regions. With reliability in mind, Ecogreen high efficiency heat pumps are designed to be completely serviceable, easy to install and maintain, with redundancy of components & power, smart electronic control, monitoring & BACnet communication.
The economy, fossil fuel crisis and global warming, demands not only more efficiency and rough equipment, demands heating produced by heat pumps instead fossil fuel boilers, but not only heating production, also recover the heat produced by AC systems when this run-in cooling mode.
- Showers
- Comfort Heating
- Pools
- Humidity Room Control and Dehumidification Reheat Coils
Our Goals Netzero GWP Impact like our Scroll ASHP R290 Natural Refrigerant, and on the mid term LOW GWP NextGen Refrigerants as R454B,R454C,R32, A1 R513

Glossary
ASHP – Air Source Heat Pump.
WSHP – Water Source Heat Pump.
2-pipe – Hot or cold entering and leaving water connections.
4-pipe – Hot and cold water independent circuits.
Reversible – Heats or cools your water loop.
Partial HR – Partial Heat Recovery.
Full HR – Full Heat Recovery.
Recip. – Reciprocating Semi-hermetic Compressor.
Screw – Helical Screw Semi-hermetic Compressor.
Scroll – Scroll Hermetic Compressor.
AIM Act – The American Innovation and Manufacturing Act.
EPA– United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Next-gen refrigerants. – HFC & HFO drop-in replacement refrigerants, pure or blends that are low GWP.
HFCs – Hydrofluorocarbons are potent GHGs intentionally developed as replacements for ODS.
GHGs – Greenhouse Gases.
ODS – Ozone-depleting substances.
GWP – Global Warming Potential, a measure of the climate impact of a GHG relative to that of CO2.
Net Zero – Carbon neutrality / zero carbon dioxide emissions.
Decarbonization – Climate change mitigation by reducing emissions of greenhouse gases.
Electrification – powering by electricity and changing over from an earlier power source.